What is a Robotic Welder
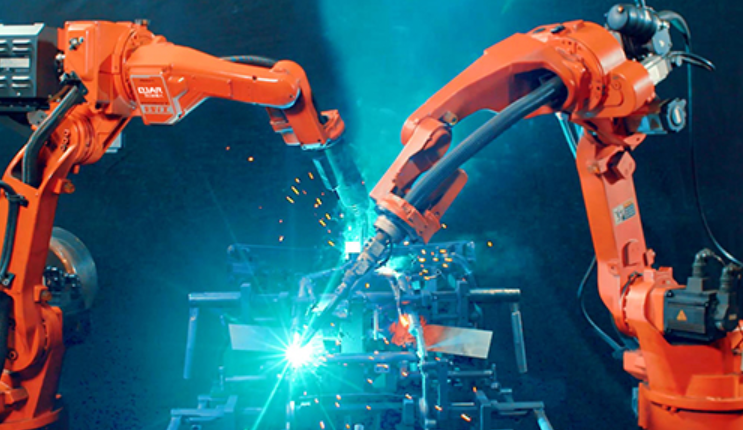
Automation is transforming modern manufacturing, making production faster, safer, and more precise. A robotic welder is an automated machine that performs welding tasks using robotic arms, sensors, and software. It joins metal parts with high accuracy and consistency, follows precise weld paths, and can operate continuously without fatigue.
Understanding robotic welding is essential for businesses today, as it enhances productivity, delivers consistent high-quality results, minimizes waste, and helps companies stay competitive in a rapidly evolving industrial landscape.
What is a Robotic Welder?
A robotic welder is an automated system that uses programmable robotic arms, sensors, and specialized software to perform welding tasks such as MIG, TIG, and spot welding with high precision and consistency. These systems can handle complex shapes and varying materials to ensure optimal weld quality.
Key Capabilities
- High-Precision Welding: Follows exact weld paths and adjusts in real time for consistent quality.
- Continuous Operation: Works without fatigue, increasing productivity and reducing cycle times.
- Adaptability: Robots handle complex shapes and varied materials using advanced sensors.
Core Components
- Robotic Arm: Moves the welding torch along precise paths.
- Welding Torch: Delivers the arc and filler material.
- Power Supply: Provides energy for welding.
- Wire Feeder: Supplies filler material as needed.
- Sensors & Vision Systems: Guide the robot and ensure accurate welds.
- Controller: Manages movements and welding parameters.
Robotic welding helps businesses boost productivity, improve weld quality, and maintain safety in manufacturing.
See also: Top Reasons to Trust Hi Tech Data Group for Data Recovery in Kenya
Types of Robotic Welders
Robotic welding systems are built for different welding processes, each tailored to specific applications. The main types include:
- Arc Welding Robots
These robots use an electric arc to melt metal and form strong, durable joints. They work best with thick materials and are commonly used in industries like shipbuilding and heavy equipment manufacturing.
- Spot Welding Robots
Spot welding robots join metal sheets at precise points using heat and pressure. Their speed and accuracy make them perfect for high-volume production, such as automobile assembly.
- Laser Welding Robots
Laser welding robots employ a focused laser beam to melt and fuse materials. They offer exceptional precision and speed, making them suitable for delicate applications like small electronics, medical devices, or detailed components.
Each type of robotic welder enhances efficiency, precision, and safety, meeting the unique needs of different industries.
How Does a Robotic Welder Work?
Components and How They Work
Robotic welding systems use several key parts to automate welding with precision:
- Robotic Arm (Manipulator): A six-axis arm that moves the welding torch along exact paths.
- Welding Torch: Delivers the welding arc and filler material to join metal parts.
- Power Supply: Controls the electricity to maintain a stable arc and high-quality welds.
- Wire Feeder: Supplies the filler material at a steady rate for consistent welds.
- Sensors and Cameras: Track the welding process in real time, enabling the system to make automatic adjustments for precise and consistent welds.
- Controller: The “brain” of the system, coordinating all parts and following programmed instructions.
Efficiency and Precision
Robotic welders work continuously without fatigue, increasing productivity compared to humans. They follow programmed controls to adjust speed, arc length, and heat input, creating welds accurate to fractions of a millimeter.
Real-time sensors track the weld seam and make adjustments as needed, ensuring consistent, high-quality results. Robots can also reach difficult positions and maintain the correct torch angle, preventing defects like porosity or incomplete fusion.
Benefits of Using a Robotic Welder
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency
Robotic welders work faster and more consistently than humans. They can operate for long periods without breaks, handle 50–90% of welding tasks depending on production type, and a single robotic cell can replace several human welders. This boosts production speed and overall throughput.
- Consistent Quality and Precision
Robots deliver highly accurate and repeatable welds, reducing errors and defects that often occur with manual welding. Real-time monitoring detects faults immediately, ensuring high-quality, consistent results.
- Reduction in Waste and Consumable Usage
Robotic welders precisely control welding parameters, using only the required amount of material. This minimizes spatter, over-welding, and material waste, while also reducing the need for rework, saving both materials and labor.
Robotic welding improves productivity, maintains high-quality standards, and lowers costs, making manufacturing more efficient and reliable.
Industries That Use Robotic Welders
Robotic welding systems have changed manufacturing by improving precision, efficiency, and safety. Here’s how major industries are benefiting:
- Automotive Manufacturing
The automotive industry is a pioneer in robotic welding, using robots for tasks such as spot welding, arc welding, and assembly. About 30% of all industrial robots operate in car factories, boosting production speed and accuracy while improving worker safety by taking on hazardous tasks.
- Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace, robots ensure the structural strength of essential components like fuselage panels, wing spars, and landing gear. Their precision and reliability meet the strict quality standards required in this sector.
- Construction and Heavy Machinery
In construction and heavy machinery, robots are used to weld steel structures, bridges, and machine parts. They create strong, accurate, and long-lasting welds, which improve the safety and stability of large construction projects.
- Electronics and Consumer Goods
In the electronics industry, robots handle the welding of metal parts for devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computer cases. Automation ensures the welds are fast, precise, and consistent, allowing manufacturers to meet high production demands while maintaining top-quality standards.
Robotic welding boosts production, improves quality, and enhances safety, helping industries stay competitive.
The Future of Robotic Welders
Robotic welding is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), collaborative robots (cobots), and a growing focus on sustainability. These trends are shaping smarter, safer, and more efficient welding processes.
AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are transforming robotic welding by enabling:
- Adaptive Welding: Systems analyze real-time data to adjust welding parameters, ensuring consistent, high-quality welds.
- Predictive Maintenance: Machine learning predicts equipment failures before they happen, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Automated Path Planning: AI optimizes welding paths, cutting setup times, and improves efficiency.
These innovations make welding operations more intelligent, productive, and cost-effective.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Cobots are designed to work safely alongside humans, offering:
- Enhanced Safety: Sensors detect human presence and adjust movements to prevent accidents.
- Easy Integration: User-friendly interfaces and flexible programming make cobots accessible to small and medium-sized businesses.
- Higher Productivity: Cobots handle repetitive welding tasks, freeing human workers to concentrate on more complex and skilled operations.
By making robotic welding more accessible, cobots enable businesses of all sizes to adopt automation.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
The welding industry is increasingly focusing on environmentally friendly and energy-efficient practices:
- Eco-Friendly Welding: Techniques like battery-powered welders, laser welding, and friction stir welding reduce energy consumption and emissions.
- Energy-Efficient Equipment: Modern machines use less power and have longer operational lifespans.
- Waste Reduction: Advanced processes minimize material waste and improve recycling.
These trends not only support environmental responsibility but also reduce costs and enhance operational efficiency.






